Γ(z) Returns the value of the Euler gamma function
of z. (To type Γ,
press G[Ctrl]G.)
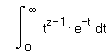
Γ(a, x) Returns the value of the incomplete gamma
function of x with parameter a.
Γ(a,0) = Γ(a).
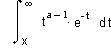
lnΓ(z) Returns the natural log of the Euler gamma
function, evaluated at z.
Arguments:
- z is a dimensionless, real or complex scalar,
undefined for z = 0, −1, −2...
In the case
of Γ, only arguments −107
≤ Re(z) ≤ 171 and −106 ≤
Im(z) ≤ 106 can be evaluated without numerical overflow.
- a is a dimensionless, positive, real scalar.
- x is a dimensionless, positive, real scalar, or 0.
Notes:
- The following relationships involving the gamma functions may be useful:
Γ(z + 1) = z Γ(z)
Γ(z)·Γ(1 − z) = π·csc(π·z)
Γ(n + 1) = n!
- For complex z, Γ(z) is the analytic continuation
of the real function.
- You can evaluate Γ(z) over a larger numerical
floating point range using live symbolics,
or use the lnΓ function to return smaller results,
then scale them.