Back to Contents
Set Up Profile Security: Intel(R) PRO/Wireless 3945ABG Network
Connection User Guide
Use Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Software
Personal Security
Personal Security Settings
Set up Data Encryption and Authentication
Enterprise Security
Enterprise Security Settings
Use Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Software
The following sections describe how to use Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless to set up the required security settings for your wireless adapter. Refer to Personal Security.
It also provides information about how to configure advanced security settings for your wireless adapter. This requires information from a systems administrator (corporate environment) or advanced security settings on your access point (for home users). Refer to Enterprise Security.
For general information about security settings, refer to Security Overview.
Personal Security
Use Personal Security if you are a home or small business user who can use a variety of simple security procedures to protect your wireless connection. Select from the list of security settings that do not require extensive infrastructure setup for your wireless network. A RADIUS or AAA server is not required.
- Review the Set up Data Encryption and Authentication information to learn about the different security types.
- To add or change the required security settings, click Security Settings for information to set security for the selected wireless network.
- See Profile Management for a description of when to use the Profile Wizard.
- See Security Overview for more information about the different security options for wireless networks.
- If you want to verify the security settings, select a wireless network in the Wireless Networks list. Click Details to review the operating mode, authentication level and data encryption.
- See Enterprise Security to set 802.1x authentication security.
Personal Security Settings
Personal Security Settings Description
Name |
Setting |
Personal Security |
Select to open the Personal Security settings. The security settings that are available are dependent on the Operating Mode selected in the Profile Wizard: Device to Device (ad hoc) or Network (Infrastructure). |
Data Encryption |
If you configure a profile for a Device to Device (ad hoc) network, select
If you configure an profile for an Infrastructure network, select:
|
None WEP CKIP TKIP AES-CCMP
Advanced |
Select to access the Advanced Settings to configure the following options:
|
Back |
View the prior page in the Profile Wizard. |
OK |
Closes the Profile Wizard and saves the profile. |
Cancel |
Closes the Profile Wizard and cancels any changes made. |
Help? |
Provides the help information for the current page. |
Set up Data Encryption and Authentication
In a home wireless network, you can use a variety of simple security procedures to protect your wireless connection. These include:
- Enable Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
- Change your password
- Change the network name (SSID)
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) encryption provides protection for your data on the network. WPA uses an encryption key called a Pre-Shared Key (PSK) to encrypt data before transmission. Enter the same password in all of the computers and access points in your home or small business network. Only devices that use the same encryption key can access the network or decrypt the encrypted data transmitted by other computers. The password automatically initiates the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) for the data encryption process.
Network Keys
WEP encryption provides two levels of security:
- 64-bit key (sometimes referred to as 40-bit)
- 128-bit key (also known as 104-bit)
For improved security, use a 128-bit key. If you use encryption, all wireless devices on your wireless network must use the same encryption keys.
You can create the key yourself and specify the key length (64- or 128-bit) and key index (the location that a specific key is stored). The greater the key length, the more secure the key.
Key Length: 64-bit
Pass phrase (64-bit): Enter five (5) alphanumeric characters, 0-9, a-z or A-Z.
Hex key (64-bit): Enter 10 hexadecimal characters, 0-9, A-F.
Key Length: 128-bit
Pass phrase (128-bit): Enter 13 alphanumeric characters, 0-9, a-z or A-Z.
Hex key (128-bit): Enter 26 hexadecimal characters, 0-9, A-F.
With 802.11, a wireless station can be configured with up to four keys (the key index values are 1, 2, 3, and 4). When an access point or a wireless station transmits an encrypted message that uses a key stored in a specific key index, the transmitted message indicates the key index that was used to encrypt the message body. The receiving access point or wireless station can then retrieve the key that is stored at the key index and use it to decode the encrypted message body.
Personal Security: Configure Profiles for Device to Device (Ad Hoc) Networks
Set up a Client with Open Authentication and No Data Encryption (None)
In device to device mode, also called ad hoc mode, wireless computers send information directly to other wireless computers. You can use ad hoc mode to network multiple computers in a home or small office, or to set up a temporary wireless network for a meeting.
On the Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless main window, select one of the following methods to connect to a device to device network:
- Double-click a ad hoc network in the Wireless Networks list.
- Select a network in the Wireless Networks list. Click Connect. The Intel PROSet/Wireless software automatically detects the security settings for the wireless adapter.
- Create a device to device (ad hoc) network profile as described below.
NOTE: Device to Device (ad hoc) networks are identified with a notebook image ( ) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
To create a profile for a wireless network connection with no encryption:
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add to open the Create Wireless Profile General Settings.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Operating Mode: Click Device to Device (ad hoc).
- Click Next.
- Click Personal Security to open the Security Settings.
- Data Encryption: The default setting is None, which indicates that there is no security on this wireless network.
- Click OK. The profile is added to the Profiles list and connects to the wireless network.
Set up a Client with WEP 64-bit or WEP 128-bit Data Encryption
When WEP data encryption is enabled, a network key or password is used for encryption.
You must enter the key and specify the length (64- or 128-bit) and key index (the location that a specific key is stored). The more complex the key (mixed letters and numbers), the more secure the key.
To add a network key to a device to device network connection:
- On the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window, double-click a Device to Device (ad hoc) network in the Wireless Networks list or select the network and click Connect.
When connected, a profile is added to the Profiles list.
NOTE: Device to Device (ad hoc) networks are identified with a notebook image ( ) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
- Click Profiles to access the Profiles list. Select the network that you connected to in Step 1.
- Click Properties to open the Wireless Profile Properties' General Settings. The Profile name and Wireless Network Name (SSID) display. Device to Device (ad hoc) should be selected as the Operating Mode.
- Click Next to access the Security Settings.
- Click Personal Security.
- Security Settings: The default setting is None, which indicates that there is no security on this wireless network.
To add a password or network key:
- Security Settings: Select either WEP 64-bit or WEP 128-bit to configure WEP data encryption with a 64- or 128-bit key.
When WEP encryption is enabled on a device, the WEP key is used to verify access to the network. If the wireless device does not have the correct WEP key, even though authentication is successful, the device is unable to transmit data.
- Password: Enter the Wireless Security Password (Encryption Key).
- Pass phrase (64-bit): Enter five (5) alphanumeric characters, 0-9, a-z or A-Z.
- WEP key (64-bit): Enter 10 hexadecimal characters, 0-9, A-F.
- Pass phrase (128-bit): Enter 13 alphanumeric characters, 0-9, a-z or A-Z.
- WEP key (128-bit): Enter 26 hexadecimal characters, 0-9, A-F.
- Key Index: Up to four passwords may be specified by changing the Key Index.
- To add more than one password:
- Select the Key Index number: 1, 2, 3, or 4.
- Enter the Wireless Security Password.
- Select another Key Index number.
- Enter another Wireless Security Password.
- Click OK to return to the Profiles list.
Personal Security: Configure Profiles for Infrastructure Networks
An infrastructure network consists of one or more access points and one or more computers with wireless adapters installed. Each access point must have a wired connection to a wireless network. For home users, this is usually a broadband or cable network.
Set up a Client with No (None) Data Encryption
On the Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless main window, select one of the following methods to connect to an Infrastructure network:
Set up a Client with WEP 64-bit or WEP 128-bit Data Encryption
When WEP data encryption is enabled, a network key or password is used for encryption.
A network key is provided for you automatically (for example, it might be provided by your wireless network adapter manufacturer), or you can enter it yourself and specify the key length (64- or 128-bit), key format (ASCII characters or hexadecimal digits), and key index (the location where a specific key is stored). The greater the key length, the more secure the key.
To add a network key for an Infrastructure network connection:
- On the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window, double-click an Infrastructure network in the Wireless Networks list or select the network and click Connect.
NOTE: Infrastructure networks are identified with an access point image ( ) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
- Click Profiles to access the Profiles list.
- Click Properties to open the Wireless Profile Properties' General Settings. The Profile name and Wireless Network Name (SSID) display. Network (Infrastructure) should be selected as the Operating Mode.
- Click Next to access the Security Settings.
- Security Settings: The default setting is None, which indicates that there is no security on this wireless network.
To add a password or network key:
- Security Settings: Select either WEP 64-bit or WEP 128-bit to configure WEP data encryption with a 64- or 128-bit key.
When WEP encryption is enabled on an access point, the WEP key is used to verify access to the network. If the wireless device does not have the correct WEP key, even though authentication is successful, the device is unable to transmit data through the access point or decrypt data received from the access point.
- Password: Enter the Wireless Security Password (Pass phrase) or Encryption Key (WEP key).
- Pass phrase (64-bit): Enter five (5) alphanumeric characters, 0-9, a-z or A-Z.
- WEP key (64-bit): Enter 10 hexadecimal characters, 0-9, A-F.
- Pass phrase (128-bit): Enter 13 alphanumeric characters, 0-9, a-z or A-Z.
- WEP key (128-bit): Enter 26 hexadecimal characters, 0-9, A- F.
- Key Index: Change the Key Index to set up to four passwords.
To add more than one password:
- Select the Key Index number: 1, 2, 3, or 4.
- Enter the Wireless Security Password.
- Select another Key Index number.
- Enter another Wireless Security Password.
- Click OK to return to the Profiles list.
Set up a Client with WPA-Personal (TKIP) or WPA2-Personal (TKIP) Security Settings
WPA Personal Mode requires manual configuration of a pre-shared key (PSK) on the access point and clients. This PSK authenticates users a password or identifying code, on both the client station and the access point. An authentication server is not needed. WPA Personal Mode is targeted to home and small business environments.
WPA2 is the second generation of WPA security that provides enterprise and consumer wireless users with a high level of assurance that only authorized users can access their wireless networks. WPA2 provides a stronger encryption mechanism through Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), which is a requirement for some corporate and government users.
To configure a profile with WPA-Personal network authentication and TKIP data encryption:
- On the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window, double-click an Infrastructure network in the Wireless Networks list or select the network and click Connect.
NOTE: Infrastructure networks are identified with an access point image ( ) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
- Click Profiles to access the Profiles list.
- Click Properties to open the Wireless Profile Properties' General Settings. The Profile name and Wireless Network Name (SSID) display. Network (Infrastructure) should be selected as the Operating Mode.
- Click Next to access the Security Settings.
- Security Settings: Select WPA-Personal (TKIP) to provide security to a small business network or home environment. A password, called a pre-shared key (PSK), is used. The longer the password, the stronger the security of the wireless network.
If your wireless access point or router supports WPA2-Personal then you should enable it on the access point and provide a long, strong password. The longer the password, the stronger the security of the wireless network. The same password entered in the access point needs to be used on this computer and all other wireless devices that access the wireless network.
NOTE: WPA-Personal and WPA2-Personal are not interoperable.
- Wireless Security Password (Encryption Key): Enter a text phrase with eight to 63 characters. Verify that the network key matches the password in the wireless access point.
- Click OK to return to the Profiles list.
Set up a Client with WPA-Personal (AES-CCMP) or WPA2-Personal (AES-CCMP) Security Settings
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a security enhancement that strongly increases the level of data protection and access control to a wireless network. WPA enforces 802.1x authentication and key-exchange and only works with dynamic encryption keys. For a home user or small business, WPA-Personal utilizes either Advanced Encryption Standard - Counter CBC-MAC Protocol (AES-CCMP) or Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP).
To configure a profile with WPA2-Personal network authentication and AES-CCMP data encryption:
- On the Profile page, select a profile.
- Click Properties to open the Wireless Profile Properties' General Settings. The Profile name and Wireless Network Name (SSID) display. Network (Infrastructure) should be selected as the Operating Mode.
- Click Next. The Security Settings page opens.
- Security Settings: Select WPA-Personal (AES-CCMP) to provide this level of security in the small network or home environment. It uses a password also called a pre-shared key (PSK). The longer the password, the stronger the security of the wireless network.
AES-CCMP (Advanced Encryption Standard - Counter CBC-MAC Protocol) is the new method for privacy protection of wireless transmissions specified in the IEEE 802.11i standard. AES-CCMP provides a stronger encryption method than TKIP. Choose AES-CCMP as the data encryption method whenever strong data protection is important.
If your Wireless access point or router supports WPA2-Personal then you should enable it on the access point and provide a long, strong password. The same password entered into access point needs to be used on this computer and all other wireless devices that access the wireless network.
NOTE: WPA-Personal and WPA2-Personal are not interoperable.
Some security solutions may not be supported by your computer's operating system. You may require additional software or hardware as well as wireless LAN infrastructure support. Contact your computer manufacturer for details.
Set Password:
- Wireless Security Password (Encryption Key). Enter a text phrase (length is between eight and 63 characters). Verify that the network key used matches the wireless access point key.
- Click OK to return to the Profiles list.
Back to Top
Back to Contents
Enterprise Security
From the Security Settings page you can enter the required security settings for the selected wireless network.
Use Enterprise Security if your network environment requires 802.1x authentication.
Enterprise Security Settings
Enterprise Security Settings Description
Name |
Setting |
Enterprise Security |
Select to open the Enterprise Security settings. The security settings that are available are dependent on the Operating Mode selected: Device to Device (ad hoc) or Network (Infrastructure). |
Network Authentication |
If you configure a Device to Device (ad hoc) profile, the default is Open authentication.
If you configure an Infrastructure profile, select:
|
Data Encryption |
|
Enable 802.1x (Authentication Type) |
Click to open the following 802.11x authentication types:
|
Cisco Options |
Click to view the Cisco Compatible Extensions.
NOTE: Cisco Compatible Extensions are automatically enabled for CKIP and LEAP profiles. |
Advanced button |
Select to access the Advanced Settings to configure the following options:
|
Back |
View the prior page in the Profile Wizard. |
Next |
View the next page in the Profile Wizard. If more security information is required then the next Step of the Security page is displayed. |
OK |
Closes the Profile Wizard and saves the profile. |
Cancel |
Closes the Profile Wizard and cancels any changes made. |
Help? |
Provides the help information for the current page. |
Enterprise Security: Configure Profiles for Device to Device (Ad Hoc) Networks
Set up a Client with Open Network Authentication and No (None) Data Encryption
When Open authentication is used, any wireless station can request authentication. The station that needs to authenticate with another wireless station sends an authentication management frame that contains the identity of the sending station. The receiving station grants any request for authentication. Open authentication allows any device network access. If no encryption is enabled on the network, any device that knows the SSID can gain access to the network.
In Device to Device (ad hoc) mode, wireless computers send information directly to other wireless computers. You can use ad hoc mode to network multiple computers in a home or small office, or to set up a temporary wireless network for a meeting.
- On the Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless main window, select one of the following methods to connect to a device to device network:
- Double-click a Device to Device (ad hoc) network in the Wireless Networks list.
- Select a Device to Device (ad hoc) network in the Wireless Networks list. Click Connect. The Intel PROSet/Wireless software automatically detects the security settings for the wireless adapter.
NOTE: Device to Device (ad hoc) networks are identified with a notebook image ( ) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
To create a profile for a wireless network connection with no encryption:
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add to open the
Create Wireless
Profile General Settings.
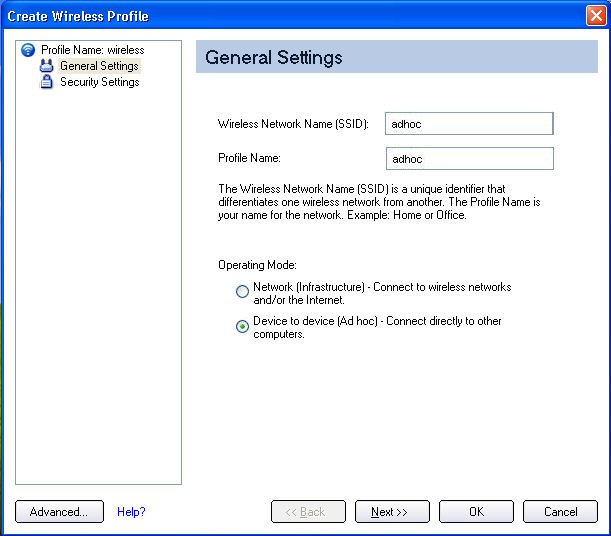
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Operating Mode: Click Device to Device (ad hoc).
- Click Next
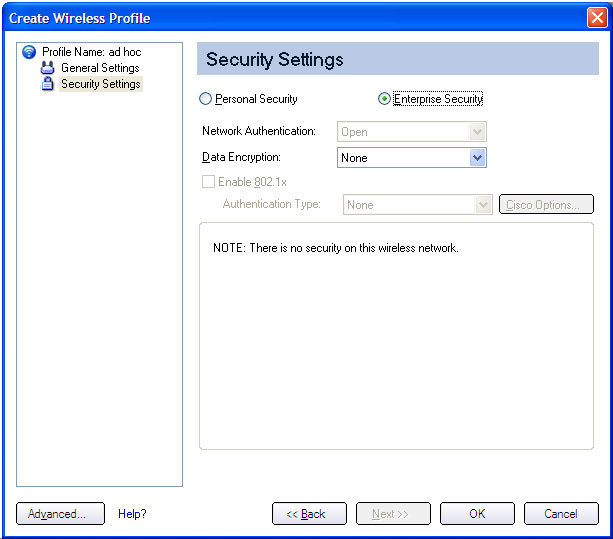
- Click Enterprise Security to open the Security Settings.
- Network Authentication: Open (Selected).
When Open authentication is used, any wireless station can request authentication. The station that needs to authenticate with another wireless station sends an authentication management frame that contains the identity of the sending station. T he receiving station grants any request for authentication. Open authentication allows any device network access. If no encryption is enabled on the network, any device that knows the SSID can gain access to the network. Device to Device (ad hoc) networks always operate with Open authentication.
- Data Encryption: None is the default.
- Click OK. The profile is added to the Profiles list and connects to the wireless network.
Set up a Client with Open Network Authentication and WEP Data Encryption
On the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window, select one of the following methods to connect to a device to device network:
- Double-click a Device to Device (ad hoc) network in the Wireless Networks list.
- Select a Device to Device (ad hoc) network in the Wireless Networks list. Click Connect. The Intel PROSet/Wireless software automatically detects the security settings for the wireless adapter.
NOTE: Device to Device (ad hoc) networks are identified with a notebook image ( ) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
- If Data Encryption is required, you may select WEP. You are asked to select either a 64-bit or 128-bit encryption level Security Password (Encryption Key) and a Key Index. These values must match the various devices in your device to device (ad hoc) network, or data is not transferred.
NOTE: If you need to edit or change the wireless network settings, refer to Profile Management for more information.
To create a profile for a wireless network connection with WEP encryption:
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add to open the
Create Wireless
Profile Wizard's General Settings.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Operating Mode: Click Device to Device (ad hoc).
- Click Next.
- Click Enterprise Security to open the Security Settings.
- Network Authentication: Open is selected (Default).
Ad hoc networks only use Open authentication.
- Data Encryption: Select WEP. WEP data encryption can be configured with 64- or 128-bit key.If the wireless device does not have the correct WEP key, the device is unable to transmit or decrypt data.
- Encryption Level: Select 64- or 128-bit.
- Wireless Security Password (Encryption Key):
Enter the wireless network Password (WEP Key). The Password is the same value used by the wireless access point or router. Contact your administrator for this password.
- Pass phrase (64-bit): Enter five (5) alphanumeric characters, 0-9, a-z, or A-Z.
- Hex key (64-bit): Enter 10 hexadecimal characters, 0-9, A-F.
- Pass phrase (128-bit): Enter 13 alphanumeric characters, 0-9, a-z, or A-Z.
- Hex key (128-bit): Enter 26 hexadecimal characters, 0-9, A-F.
- Key Index: Select 1, 2, 3, or 4. Up to four passwords may be specified by changing the Key Index.
To change the security settings:
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window. The network that you just connected to is listed in the Profiles list.
- Select the wireless network.
- Click Properties to open the Wireless Profile Properties General Settings. The Wireless Network Name (SSID) and Profile Name are already defined. Device to Device (ad hoc) is selected as the operating mode.
- Click Next to access the Security Settings.
- Click Enterprise Security.
- Network Authentication: Open is the default. No authentication is used.
- Data Encryption: WEP is selected. You can change the WEP key, key index or encryption level.
- Click OK to return to the Profiles list after you have completed your changes.
Enterprise Security: Configure Profiles for Infrastructure Networks
An infrastructure network consists of one or more access points and one or more computers with wireless adapters installed. Each access point must have a wired connection to a wireless network.
Set up a Client with No Authentication or Data Encryption (None)
On the Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless main page, select one of the following methods to connect to an Infrastructure network:
- Double-click an Infrastructure network in the Wireless Networks list.
- Select an Infrastructure network in the Wireless Networks list. Click Connect. The Intel PROSet/Wireless software automatically detects the security settings for the wireless adapter.
If there is no authentication required, the network connects without a prompt to enter any log-on credentials. Any wireless device with the correct network name (SSID) is able to associate with other devices in the network.
To create a profile for a wireless network connection with no encryption:
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add to open the Create Wireless Profile General Settings.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Operating Mode: Click Network (Infrastructure)
- Click Next.
- Click Enterprise Security to open the Security Settings.
- Network Authentication: Open (Selected).
Open authentication allows a wireless device access to the network without 802.11 authentication. If no encryption is enabled on the network, any wireless device with the correct network name (SSID) can associate with an access point and gain access to the network.
- Data Encryption: None is the default.
- Click OK. The profile is added to the Profiles list and connects to the wireless network .
Set up a Client with Shared Network Authentication
When Shared Key authentication is used, each wireless station is assumed to have received a secret shared key over a secure channel that is independent from the 802.11 wireless network communications channel. Shared key authentication requires that the client configure a static WEP or CKIP key. The client access is granted only if it passes a challenge-based authentication. CKIP provides stronger data encryption than WEP, but not all operating systems and access points support it.
NOTE: While shared key would appear to be the better option for a higher level of security, a known weakness is created by the clear text transmission of the challenge string to the client. Once an invader finds the challenge string, the shared authentication key can be easily reverse engineered. Therefore, open authentication is actually, and counter intuitively, more secure.
To create a profile with shared authentication:
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile Page, click Add to open the Create Wireless Profile General Settings.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Operating Mode: Click Network (Infrastructure).
- Click Next to access the Security Settings.
- Click Enterprise Security.
- Network Authentication: Select Shared. Shared authentication is accomplished with a pre-configured WEP key.
- Data Encryption: Select None, WEP (64- or 128-bit), or CKIP (64- or 128-bit).
- Enable 802.1x: Disabled.
- Encryption Level: 64- or 128-bit: When switching between 64- and 128-bit encryption, the previous settings are erased and a new key must be entered.
- Key Index: Select 1,2, 3, or 4. Change the Key Index to specify up to four passwords.
- Wireless Security Password (Encryption Key): Enter the wireless network password (WEP Encryption Key). This password is the same value used by the wireless AP or router. Contact your administrator for this password.
- Pass phrase (64-bit): Enter five (5) alphanumeric characters, 0-9, a-z or A-Z.
- Hex key (64-bit): Enter 10 hexadecimal characters, 0-9, A-F.
- Pass phrase (128-bit): Enter 13 alphanumeric characters, 0-9, a-z or A-Z.
- Hex key (128-bit): Enter 26 hexadecimal characters, 0-9, A-F.
Set up a Client with WPA-Personal or WPA2-Personal Network Authentication
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a security enhancement that strongly increases the level of data protection and access control to a wireless network. WPA enforces key-exchange and only works with dynamic encryption keys. If your wireless AP or router supports WPA-Personal and WPA2-Personal then you should enable it on the AP and provide a long, strong password. For personal or home networks
without a RADIUS or AAA server, use Wi-Fi Protected Access Personal.
- WPA-Personal: A wireless security method that provides strong data protection and prevents unauthorized network access for small networks. It uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) encryption or AES-CCMP and protects against unauthorized network access through the use of a pre-shared key (PSK).
- WPA2-Personal: A follow-on wireless security method to WPA that provides stronger data protection and prevents unauthorized network access for small networks.
NOTE: WPA-Personal or WPA2 Personal are not interoperable.
Some security solutions may not be supported by your computer's operating system and may require additional software or certain hardware as well as wireless LAN infrastructure support. Check with your computer manufacturer for details.
To add a profile with WPA-Personal or WPA2-Personal network authentication:
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add to open the Profile Wizard's General Settings.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Operating Mode: Click Network (Infrastructure).
- Click Next to access the Security Settings.
- Click Enterprise Security.
- Network Authentication: Select WPA-Personal or WPA2-Personal. See Security Overview.
- Data Encryption: Select one of the following:
- TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message integrity check and a rekeying mechanism.
- AES-CCMP (Advanced Encryption Standard - Counter CBC-MAC Protocol) is used as the data encryption method whenever strong data protection is important.
- Password: Enter a text phrase from 8 to 63 characters. The longer the password, the stronger the security of the wireless network. The same password entered into an access points needs to be used on this computer and all other wireless devices that access the wireless network.
Set up a Client with WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise Network Authentication
WPA2-Enterprise requires an authentication server.
- WPA-Enterprise: A wireless security method that provides strong data protection for multiple users and large managed networks. It uses the 802.1X authentication framework with TKIP encryption and prevents unauthorized network access by verifying network users through an authentication server.
- WPA2-Enterprise: The follow-on wireless security method to WPA that provides stronger data protection for multiple users and large managed networks. It prevents unauthorized network access by verifying network users through an authentication server.
NOTE: WPA-Enterprise and WPA2-Enterprise are not interoperable.
To add a profile that uses WPA - Enterprise or WPA2 - Enterprise authentication:
- Obtain a user name and password on the RADIUS server from your administrator.
- Certain Authentication Types require that obtain and install a client certificate. Refer to Setting up the Client for TLS authentication or consult your administrator.
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add to open the Profile Wizard's General Settings.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Operating Mode: Click Network (Infrastructure).
- Click Next.
- Click Enterprise Security.
- Network Authentication: Select WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise.
- Data Encryption: Select one of the following:
- TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message integrity check and a rekeying mechanism.
- AES-CCMP (Advanced Encryption Standard - Counter CBC-MAC Protocol) is used as the data encryption method whenever strong data protection is important. AES-CCMP is recommended.
- Enable 802.1x: Selected.
- Authentication Type: Select one of the following: EAP-SIM, LEAP, TLS, TTLS, PEAP, EAP-FAST.
Set up a Client with WEP Data Encryption and MD5 Network Authentication
MD5 authentication is a one-way authentication method that uses user names and passwords. This method does not support key management, but does require a pre-configured key if data encryption is used. To add WEP and MD5 authentication to a new profile:
NOTE: Before you begin, you need to know the user name and password on the RADIUS server that grants access to the network.

- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add to open the Profile Wizard's General Settings.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Operating Mode: Click Network (Infrastructure).
- Click Next.
- Click Enterprise Security.
- Network Authentication: Select Open (Recommended).
- Data Encryption: Select WEP.
- Click 802.1x Enabled.
- Authentication type: Select MD5.
Step 1 of 2: Password
- Encryption Level: Select either 64- or 128-bit.
- Wireless Security Password (Encryption Key): Enter your network key (wireless security password) for your wireless network. Verify that the network key matches the wireless AP.
- Use pass phrase: Enter a text phrase, up to 5 (64-bit) or 13 (128-bit) alphanumeric characters (0-9, a-z or A-Z).
- Use hex key: Enter up to 10 alphanumeric characters (64-bit, 0-9, A-F) or 26 alphanumeric characters (128-bit, 0-9, A-F).
- Key Index: Select 1, 2, 3 or 4. (Default key is 1.)
- Click Next.

Step 2 of 2: MD5 User
- Select one of the following credential methods:
- Use Windows logon user name and password: The 802.1x credentials match your Windows user name and password. Before connection, you are prompted for your Windows logon credentials.
NOTE: This option is unavailable if Pre-Logon Connect is not selected during installation of the Intel PROSet/Wireless software. Refer to Install or Uninstall the Single Sign On Feature.
- Prompt for the user name and password: Prompt for your user name and password every time you log onto the wireless network.
- Use the following user name and password: Use your saved credentials to log onto the network.
- User Name: This user name must match the user name that is set in the authentication server by the administrator prior to client authentication. The user name is case-sensitive. This name specifies the identity supplied to the authenticator by the authentication protocol operating over the TLS tunnel. This identity is securely transmitted to the server only after an encrypted channel has been established.
- Domain: Name of the domain on the authentication server. The server name identifies a domain or one of its sub-domains (for example, zeelans.com, where the server is blueberry.zeelans.com). NOTE: Contact your administrator to obtain the domain name.
- Password: Specifies the user password. The password characters appear as asterisks. This password must match the password that is set in the authentication server.
- Confirm Password: Reenter the user password.
- Click OK to save the credentials.
- Click Connect to connect to the selected wireless network.
If you did not select Use Windows logon on the Security Settings page and also did not configure user credentials, an Enter Credentials message appears when you attempt to connect to this profile. Enter your user name, domain, and password. Click OK to access the profile.
- Click OK to close Intel PROSet/Wireless.
Set up a Client with WEP Data Encryption and EAP-SIM NetworK Authentication
EAP-SIM uses a dynamic session-based WEP key, which is derived from the client adapter and RADIUS server, to encrypt data. EAP-SIM requires you to enter a user verification code, or Personal Identification Number (PIN), for communication with the Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card. A SIM card is a special smart card that is used by Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) based digital cellular networks. To add a profile with EAP-SIM authentication:
- On the Profile page, click Add to open General Settings.
- Profile Name: Enter a profile name.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Operating Mode: Click Network (Infrastructure).
- Click Next to access the Security Settings.
- Click Enterprise Security.
- Network Authentication: Select Open (Recommended).
- Data Encryption: Select WEP.
- Click Enable 802.1x.
- Authentication type: Select EAP-SIM.
EAP-SIM authentication can be used with:
- Network Authentication types: Open, Shared, WPA - Enterprise and WPA2 - Enterprise
- Data Encryption types: None, WEP, TKIP, AES-CCMP and CKIP
EAP-SIM User (optional)
- Specify user name (identity): Click to specify the user name.
- User Name: Enter the user name assigned to the SIM card.
- Click OK.
Set up a Client with TLS Network Authentication
These settings define the protocol and the credentials used to authenticate a user. Transport Layer Security (TLS) authentication is a two-way authentication method that exclusively uses digital certificates to verify the identity of a client and a server.
To add a profile with TLS authentication:
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add to open the Profile Wizard's General Settings.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Type the network identifier.
- Operating Mode: Click Network (Infrastructure).
- Click Next to access the Security Settings.
- Click Enterprise Security.
- Network Authentication: Select WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise.
- Data Encryption: Select AES-CCMP (Recommended).
- Enable 802.1x: Selected.
- Authentication Type: Select TLS to be used with this connection.

Step 1 of 2: TLS User
- Obtain and install a client certificate, refer to Set up the Client for TLS authentication or consult your system administrator.
- Select one of the following to obtain a certificate:
- Use my smart card: Select if the certificate resides on a smart card.
- Use the certificate issued to this computer.
- Use a user certificate on this computer: Click Select to choose a certificate that resides on this computer.
- Click Next.

Step 2 of 2: TLS Server
Select one of the following:
- Select one of the following options:
Server name must match the specified entry exactly: When selected, the server name must match exactly the server name found on the certificate. The server name should include the complete domain name (for example, Servername.Domain name).
Domain name must end with the specified entry: When selected, the server name identifies a domain, and the certificate must have a server name that belongs to this domain or to one of its subdomains (for example, zeelans.com, where the server is blueberry.zeelans.com). NOTE: These parameters should be obtained from the administrator.
NOTE: These parameters should be obtained from the administrator.
- Click OK to save the setting and close the page.
Set up a Client with TTLS Network Authentication
TTLS authentication: These settings define the protocol and credentials used to authenticate a user. The client uses EAP-TLS to validate the server and create a TLS-encrypted channel between the client and server. The client can use another authentication protocol, typically password-based protocols (for example, MD5 Challenge over this encrypted channel to enable server validation). The challenge and response packets are sent over a non-exposed TLS encrypted channel. The following example describes how to use WPA with AES-CCMP encryption with TTLS authentication.
To set up a client with TTLS Network Authentication:
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add to open the Profile Wizard's General Settings.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Operating Mode: Click Network (Infrastructure).
- Click Next to access the Security Settings.
- Click Enterprise Security.
- Network Authentication: Select WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise.
- Data Encryption: Select one of the following:
- TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message integrity check and a rekeying mechanism.
- AES-CCMP (Advanced Encryption Standard - Counter CBC-MAC Protocol) is used as the data encryption method whenever strong data protection is important. AES-CCMP is recommended.
- Enable 802.1x: Selected.
- Authentication Type: Select TTLS to be used with this connection.
Step 1 of 2: TTLS User
- Authentication Protocol: This parameter specifies the authentication protocol operating over the TTLS tunnel. The protocols are: PAP (Default), CHAP, MD5, MS-CHAP and MS-CHAP-V2. See Security Overview for more information.
- User Credentials:
For PAP, CHAP, MD5, MS-CHAP, and MS-CHAP-V2 protocols, select one of these authentication methods:
- Use the Windows logon: Select to retrieve the user's credentials from the user's Windows logon process.
NOTE: This option is unavailable if Pre-Logon Connect is not selected during installation of the Intel PROSet/Wireless software. Refer to Install or Uninstall the Single Sign On Feature.
- Prompt each time I connect: Select to prompt for user name and password before you connect to the wireless network. The user name and password must be first set in the authentication server by the administrator.
- Use the following: The user name and password are securely (encrypted) saved in the profile.
- User Name: This user name must match the user name that is set in the authentication server.
- Domain: Name of the domain on the authentication server. The server name identifies a domain or one of its subdomains (for example, zeelans.com, where the server is blueberry.zeelans.com). NOTE: Contact your administrator to obtain the domain name.
- Password: This password must match the password that is set in the authentication server. The entered password characters display as asterisks.
- Confirm Password: Reenter the user password.
- Roaming Identity: If the Roaming Identity is cleared, %domain%\%username% is the default.
When 802.1x MS RADIUS is used as an authentication server, the server authenticates the device that uses the Roaming Identity user name from Intel PROSet/Wireless software, and ignores the Authentication Protocol MS-CHAP-V2 user name. This feature is the 802.1x identity supplied to the authenticator. Microsoft IAS RADIUS accepts only a valid user name (dotNet user) for EAP clients. When 802.1x MS RADIUS is used, enter a valid user name. For all other servers, this is optional. Therefore, it is recommended to use the desired realm (for example, anonymous@myrealm) instead of a true identity.
Step 2 of 2: TTLS Server
- Validate Server Certificate: Selected.
- Certificate Issuer: The server certificate received during the TTLS message exchange must have been issued by this certificate authority (CA). Trusted intermediate certificate authorities and root authorities whose certificates exist in the system store are available for selection. If Any Trusted CA is selected, any CA in the list is acceptable.
- Specify Server or Certificate Name: The server name or domain to which the server belongs, whichever of the following has been selected.
- Server name must match exactly: When selected, the server name entered must match exactly the server name found on the certificate. The server name should include the complete domain name (for example, Servername.Domain name).
- Domain name must end in specified name: When selected, the server name identifies a domain and the certificate must have a server name belonging to this domain or to one of its subdomains (for example, zeelans.com, where the server is blueberry.zeelans.com)
NOTE: These parameters should be obtained from the administrator.
- Click OK to save the setting and close the page.
Set up a Client with PEAP Network Authentication
PEAP authentication: PEAP settings are required for the authentication of the client to the authentication server. The client uses EAP-TLS to validate the server and create a TLS-encrypted channel between client and server. The client can use another EAP mechanism (for example, Microsoft Challenge Authentication Protocol (MS-CHAP) Version 2), over this encrypted channel to enable server validation. The challenge and response packets are sent over a non-exposed TLS encrypted channel. The following example describes how to use WPA with AES-CCMP or TKIP encryption with PEAP authentication.
To set up a client with PEAP Authentication:
Obtain and install a client certificate. Refer to Set up the Client for TLS authentication or consult your administrator.
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add to open the Profile Wizard's General Settings.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Operating Mode: Click Network (Infrastructure).
- Click Next to access the Security Settings.
- Click Enterprise Security.
- Network Authentication: Select WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise.
- Data Encryption: Select one of the following:
- TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message integrity check and a rekeying mechanism.
- AES-CCMP (Advanced Encryption Standard - Counter CBC-MAC Protocol) is used as the data encryption method whenever strong data protection is important. AES-CCMP is recommended.
- Enable 802.1x: Selected.
- Authentication Type: Select PEAP to be used with this connection.
Step 1 of 2: PEAP User
PEAP relies on Transport Layer Security (TLS) to allow unencrypted authentication types (for example, EAP-Generic Token Card (GTC) and One-Time Password (OTP) support).
- Authentication Protocol: Select either GTC, MS-CHAP-V2 (Default), or TLS. Refer to Authentication Protocols.
- User Credentials: Select one of the following:
- Use Windows Logon: Allows the 802.1x credentials to match your Windows user name and password. Before connection, you are prompted for your Windows logon credentials.
- Prompt each time I connect: Prompts for user name and password every time you log onto the network.
- Use the following: The user name and password are securely (encrypted) saved in the profile.
- User Name: This user name must match the user name that is set in the authentication server.
- Domain: Name of the domain on the authentication server. The server name identifies a domain or one of its subdomains (for example, zeelans.com, where the server is blueberry.zeelans.com). NOTE: Contact your administrator to obtain the domain name.
- Password: This password must match the password that is set in the authentication server. The entered password characters display as asterisks.
- Confirm Password: Reenter the user password.
- Roaming Identity: If the Roaming Identity is cleared, %domain%\%username% is the default.
When 802.1x MS RADIUS is used as an authentication server, the authentication server authenticates the device with the Roaming Identity user name from the Intel PROSet/Wireless utility and ignores the Authentication Protocol MS-CHAP-V2 user name. This feature is the 802.1x identity supplied to the authenticator. Microsoft IAS RADIUS accepts only a valid user name (dotNet user) for EAP clients. Enter a valid user name whenever 802.1x MS RADIUS is used. For all other servers, this is optional, therefore, it is recommended that you no use a true identity, but instead the desired realm (for example, anonymous@myrealm).
Configure Roaming Identity to support multiple users:
If you use a Pre-Logon or Common connection profile that requires the roaming identity to be based on the Windows logon credentials, the creator of the profile can add a roaming identity that uses %username% and %domain%. The roaming identity is parsed and the appropriate log on information is substituted for the keywords. This allows maximum flexibility in configuring the roaming identity while allowing multiple users to share the profile.
Please refer to your authentication server user guide for directions about how to format a suitable roaming identity. Possible formats are:
%domain%\%username%
%username%@%domain%
%username%@%domain%.com
%username%@mynetwork.com
If Roaming Identity is cleared, %domain%\%username% is the default.
Notes about the credentials: This user name and domain must match the user name that is set in the authentication server by the administrator prior to client authentication. The user name is case-sensitive. This name specifies the identity supplied to the authenticator by the authentication protocol operating over the TLS tunnel. This user identity is securely transmitted to the server only after an encrypted channel has been verified and established.
Authentication Protocols: These parameter specifies the authentication protocols that can operate over the TTLS tunnel. Below are instructions on how to configure a profile that uses PEAP authentication with GTC, MS-CHAP-V2 (Default), or TLS authentication protocols. Generic Token Card (GTC)
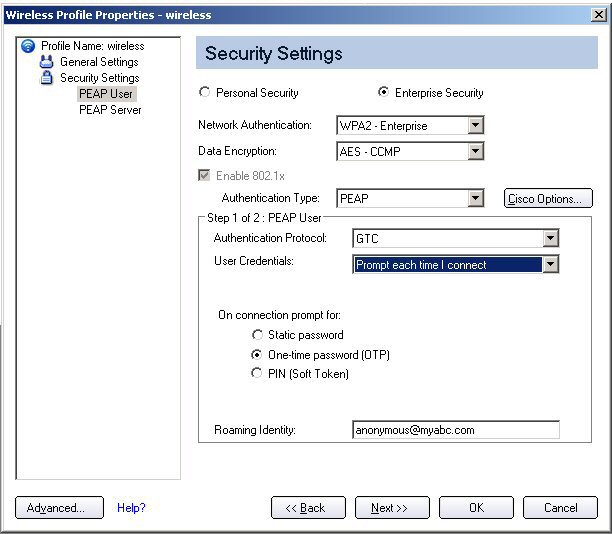
To configure a one-time password:
- Authentication Protocol: Select GTC (Generic Token Card).
- User Credentials: Select Prompt each time I connect
- On connection prompt for: Select one of the following:
- Static password: On connection, enter the user credentials.
- One-time password (OTP): Obtain the password from a hardware token device.
- PIN (Soft Token): Obtain the password from a soft token program.
- Click OK.
- Select the profile on the Wireless Networks list.
- Click Connect. When prompted, enter the user name, domain and one-time password (OTP).
- Click OK. You are asked to verify your log in information.
NOTE: The Prompt each time I connect option is unavailable if an Administrator has cleared the Cache Credentials setting in the the Administrator Tool. Refer to Administrator Settings for more information.

MS-CHAP-V2. This parameter specifies the authentication protocol operating over the PEAP tunnel.
-
User Credentials: Select one of the following options:
- Use Windows Logon: Allows the 802.1x credentials to match your Windows user name and password. Before connection, you are prompted for your Windows logon credentials.
- Prompt each time I connect: Prompts for user name and password every time you log onto the network.
- Use the following user name and password: The user name and password are securely (encrypted) saved in the profile.
- User Name: This user name must match the user name that is set in the authentication server.
- Domain: Name of the domain on the authentication server. The server name identifies a domain or one of its subdomains (for example, zeelans.com, where the server is blueberry.zeelans.com). NOTE: Contact your administrator to obtain the domain name.
- Password: This password must match the password that is set in the authentication server. The entered password characters display as asterisks.
- Confirm Password: Reenter the user password.
NOTE: This option is unavailable if Pre-Logon Connect is not selected during installation of the Intel PROSet/Wireless software. Refer to Install or Uninstall the Single Sign On Feature.
TLS: Transport Layer Security authentication is a two-way authentication method that exclusively uses digital certificates to verify the identity of a client and a server.
- Obtain and install a client certificate, refer to Set up the Client for TLS authentication or consult your system administrator.
- Select one of the following to obtain a certificate:
- Use my smart card: Select if the certificate resides on a smart card.
- Use the certificate issued to this computer: Click Select to choose a certificate that resides in the machine store.
- Use a user certificate on this computer. Click Select to choose a certificate that resides on this computer.
- Click Next.
Step 2 of 2: PEAP Server
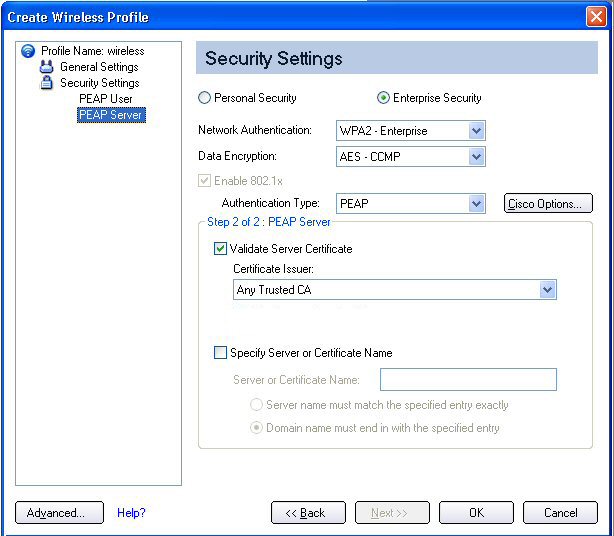
- Select one of the following options:
Server name must match the specified entry exactly: When selected, the server name must match exactly the server name found on the certificate. The server name should include the complete domain name (for example, Servername.Domain name).
Domain name must end with the specified entry: When selected, the server name identifies a domain, and the certificate must have a server name that belongs to this domain or to one of its subdomains (for example, zeelans.com, where the server is blueberry.zeelans.com). NOTE: These parameters should be obtained from the administrator.
Notes about Certificates: The specified identity should match the Issued to identity in the certificate and should be registered on the authentication server (for example, RADIUS server) that is used by the authenticator. Your certificate must be valid with respect to the authentication server. This requirement depends on the authentication server and generally means that the authentication server must know the issuer of your certificate as a Certificate Authority. Use the same user name you used to log in when the certificate was installed.
- Click OK. The profile is added to the Profiles list.
- Click the new profile at the end of the Profiles list. Use the up and down arrows to change the priority of the new profile.
- Click Connect to connect to the selected wireless network.
If you did not select Use Windows logon on the Security Settings page and also did not configure user credentials, no credentials are saved for this profile. Please enter your credentials to authenticate to the network.
- Click OK to close Intel PROSet/Wireless.
PEAP-TLS Certificate Auto Enrollment
In the Application Settings (Advanced Settings), select Intel(R) PROSet TLS Certificate Rejected Warning if you want a warning issued when a PEAP-TLS certificate is rejected.When a certificate has an invalid field expiration date, you are notified that you must take one of the following actions:A potential authentication problem for profile <profile name> has been detected. The expiration date in the associated certificate may be invalid. Choose one of the following options:
Control |
Description |
Continue with current parameters. |
Continue with the current certificate. |
Update certificate manually.
|
The Select Certificate page opens for you to choose another certificate.
|
Update certificate automatically based on the certificates in the local store. |
This option is enabled only when the local store holds one or more certificates for which the "issued to" and "issued by" fields match the current certificate and for which the "expiration date" has not expired. If you choose this option, the application selects the first valid certificate.
|
Log off to obtain certificate during log on process (this does not update the profile and only applies to certificates configured for auto enrollment). |
Logs off the user, who must obtain a proper certificate during the next
log on process. The profile must be updated to select the new certificate. |
Auto enrollment |
You are notified to: Please wait while the system is trying to obtain the certificate automatically. Click Cancel to end the certificate retrieval. |
Do not show this message again.
|
A user is able to avoid this step in subsequent sessions. The choice selected is remembered for future sessions.
|
Set up a Client with LEAP Network Authentication
Cisco LEAP (Light Extensible Authentication Protocol) is an 802.1X authentication type that supports strong mutual authentication between the client and a RADIUS server. The LEAP profiles settings include LEAP, CKIP with Rogue AP detection integration. To set up a client with LEAP Authentication:
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add. The Create Wireless Profile General Settings opens.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Operating Mode: Click Network (Infrastructure).
- Click Next to access the Security Settings.
- Click Enterprise Security.
- Network Authentication: Select WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise.
- Data Encryption: Select one of the following:
- TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message integrity check and a rekeying mechanism.
- AES-CCMP (Advanced Encryption Standard - Counter CBC-MAC Protocol) is used as the data encryption method whenever strong data protection is important. AES-CCMP is recommended.
- Enable 802.1x: Selected.
- Authentication Type: Select LEAP to be used with this connection.
- Click Cisco Options.
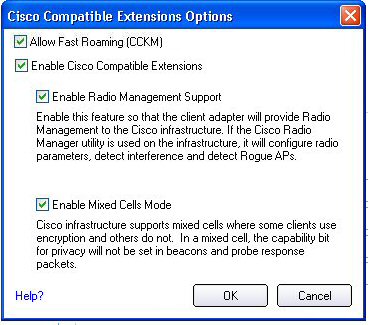
- Click Enable Cisco Compatible Extensions to enable Cisco Compatible Extensions (CCX) security (Allow Fast Roaming (CCKM), Enable Radio Management Support, Enable Mixed Cells Mode.).
- Click Enable Radio Management Support. Use Radio Management to detect rogue access points.
- Click OK to return to the Security Settings.
LEAP User:

- Select one of the following authentication methods:
- Use the Windows logon user name and password: Allows the 802.1x credentials to match your Windows user name and password. The user's credentials are retrieved from the user's Windows log-on process. The credentials are only used if the user has no password defined in the Windows log-on credentials or if there is a problem capturing the Windows log-on credentials.
NOTE: This option is unavailable if Pre-Logon Connect is not selected during installation of the Intel PROSet/Wireless software. Refer to Install or Uninstall the Single Sign On Feature.
- Prompt for the user name and password: Select to prompt for the user name and password before you connect to the wireless network. The user name and password must be first set in the authentication server by the administrator.
- Use the following user name and password: Select to save your user name and password for future use when an 802.1x authentication profile is used.
- User Name: This user name must match the user name that is set in the authentication server by the administrator prior to client authentication. The user name is case-sensitive. This name specifies the identity supplied to the authenticator by the authentication protocol. This user's identity is securely transmitted to the server only after an encrypted channel has been established.
- Domain: Name of the domain on the authentication server. The server name identifies a domain or one of its sub-domains (for example, zeelans.com, where the server is blueberry.zeelans.com). NOTE: The domain name should be obtained from the administrator.
- Password: Specifies the user password. The password characters are seen as asterisks. This password must match the password that is set in the authentication server.
- Confirm Password: Reenter the user password.
- Click OK to save the setting and close the page.
Cisco Compatible Extensions Options
Cisco Options: Use to enable or disable Radio Management and Mixed Cells Mode or Allow Fast Roaming (CCKM).
NOTE: Cisco Compatible Extensions are automatically enabled for CKIP, LEAP or EAP-FAST profiles. To override this behavior, select or clear options on this page.
- Allow Fast Roaming (CCKM): Select to enable the client wireless adapter for fast-secure roaming. When a wireless LAN is configured for fast reconnection, an EAP-FAST, EAP-TLS, PEAP-GTC, PEAP-MSCHAPv2 or LEAP-enabled client device can roam from one access point to another without involving the main server. Use Cisco Centralized Key Management (CCKM), an access point configured to provide Wireless Domain Services (WDS), to take the place of the RADIUS server and authenticate the client without perceptible delay in voice or other time-sensitive applications.
Enable Cisco Compatible Options: Select to enable Cisco Compatible Extensions for this wireless connection profile.
- Enable Radio Management Support: Select to have your wireless adapter provide radio management to the Cisco infrastructure. If the Cisco Radio Management utility is used on the infrastructure, it configures radio parameters, detects interference and rogue access points. Default setting is selected.
- Enable Mixed Cells Mode: Select to allow the wireless adapter to communicate with mixed cells. A mixed cell is a wireless network in which there are both devices that use WEP and devices that do not. Refer to Mixed Cells Mode for more information. The default setting is cleared.
Set up a Client with EAP-FAST Network Authentication
In Cisco Compatible Extensions, Version 3 (CCXv3), Cisco added support for EAP-FAST (Extensible Authentication Protocol-Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling), which uses protected access credentials (PACs) to establish an authenticated tunnel between a client and a server.
Cisco Compatible Extensions, Version 4 (CCXv4) improves the provisioning methods for enhanced security and provides innovations for enhanced security, mobility, quality of service, and network management.
Cisco Compatible Extensions, Version 3 (CCXv3)
To set up a client with EAP-FAST authentication with Cisco Compatible Extensions, version 3 (CCXv3):
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add to open the Create Wireless Profile Wizard's General Settings.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Operating Mode: Click Network (Infrastructure).
- Click Next to open the Security Settings.
- Click Enterprise Security.
- Network Authentication: Select WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise.
- Data Encryption: Select one of the following:
- TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message integrity check and a rekeying mechanism.
- AES-CCMP (Advanced Encryption Standard - Counter CBC-MAC Protocol) is used as the data encryption method whenever strong data protection is important. AES-CCMP is recommended.
- Enable 802.1x: Selected.
- Authentication Type: Select EAP-FAST to be used with this connection.

NOTE: If CCXv4 Application Setting was not installed through an Administrator Package, only EAP-FAST User settings are available for configuration. Refer to EAP-FAST User Settings.
Step 1 of 2: EAP-FAST Provisioning
- Click Disable EAP-FAST Enhancements (CCXv4) to allow provisioning inside a server-unauthenticated TLS tunnel (Unauthenticated-TLS-Server Provisioning Mode).
- Click Select server to view any unauthenticated PACs that have already been provisioned and reside on this computer.
NOTE: If the provisioned PAC is valid, Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless does not prompt the user for acceptance of the PAC. If the PAC is invalid, Intel PROSet/Wireless fails the provisioning automatically. A status message is displayed in the Wireless Event Viewer that an administrator can review on the user's computer.
To import a PAC:

- Click Select server to open the Protected Access Credentials (PAC) list.
- Click Import to import a PAC that resides on this computer or a server.
- Select the PAC and click Open.
- Enter the PAC password (optional).
- Click OK to close this page. The selected PAC is added to PAC list.
- Click Next to select the credential retrieval method or click OK to save the EAP-FAST settings and return to the Profiles list. The PAC is used for this wireless profile.
Step 2 of 2: EAP-FAST Additional Information
To perform client authentication in the established tunnel, a client sends a user name and password to authenticate and establish client authorization policy.
- Click User Credentials to select the credentials retrieval method:
- Use the Windows logon user name and password: The user credentials are retrieved from the Windows log on process.
NOTE: This option is unavailable if Pre-Logon Connect is not selected during installation of the Intel PROSet/Wireless software. Refer to Install or Uninstall the Single Sign On Feature.
- Prompt for the user name and password: Prompts for user name and password before you connect to the wireless network. The user name and password must first be set in the authentication server by the administrator.
- Use the following user name and password: The user name and password must be first set in the authentication server by the administrator.
- User Name: This user name must match the user name that is set in the authentication server.
- Domain: Name of the domain on the authentication server. The server name identifies a domain or one of its sub-domains (for example, zeelans.com, where the server is blueberry.zeelans.com). NOTE: Contact your administrator to obtain the domain name.
- Password: This password must match the password that is set in the authentication server. The entered password characters display as asterisks.
- Confirm Password: Reenter the user password.
- Click OK to save the settings and close the page. Server verification is not required.
Cisco Compatible Extensions, Version 4 (CCXv4)
To set up a client with EAP-FAST authentication with Cisco Compatible Extensions, version 4 (CCXv4):
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add to open the Create Wireless Profile Wizard's General Settings.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Operating Mode: Click Network (Infrastructure).
- Click Next to open the Security Settings.
- Network Authentication: Select WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise.
- Data Encryption: Select one of the following:
- TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message integrity check and a rekeying mechanism.
- AES-CCMP (Advanced Encryption Standard - Counter CBC-MAC Protocol) is used as the data encryption method whenever strong data protection is important. AES-CCMP is recommended.
- Data Encryption: Select AES-CCMP.
- Enable 802.1x: Selected.
- Authentication Type: Select EAP-FAST to be used with this connection.
Step 1 of 3: EAP-FAST Provisioning
With CCXv4, EAP-FAST supports two modes for provisioning:
- Server-Authenticated Mode: Provisioning inside a server authenticated (TLS) tunnel.
- Server-Unauthenticated Mode: Provisioning inside an unauthenticated (TLS) tunnel.
NOTE: Server-Authenticated Mode provides significant security advantages over Server-Unauthenticated Mode even when EAP-MSCHAPv2 is being used as an inner method. This mode protects the EAP-MSCHAPv2 exchanges from potential Man-in-the-Middle attacks by verifying the server’s authenticity before exchanging MSCHAPv2. Therefore, Server-Authenticated Mode is preferred whenever it is possible. EAP-FAST peer must use Server-Authenticated Mode whenever a certificate or public key is available to authenticate the server and ensure the best security practices.
Provisioning of Protected Access Credentials (PAC):
EAP-FAST uses a PAC key to protect the user credentials that are exchanged. All EAP-FAST authenticators are identified by an authority identity (A-ID). The local authenticator sends its AID to an authenticating client, and the client checks its database for a matching AID. If the client does not recognize the AID, it requests a new PAC.
NOTE: If the provisioned Protected Access Credential (PAC) is valid, Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless does not prompt the user for acceptance of the PAC. If the PAC is invalid, Intel PROSet/Wireless fails the provisioning automatically. A status message is displayed in the Wireless Event Viewer that an administrator can review on the user's computer.
- Verify that Disable EAP-FAST Enhancements (CCXv4) is not selected. Allow unauthenticated provisioning and Allow authenticated provisioning are selected by default. Once a PAC is selected from the Default Server, you can deselect any of these provisioning methods.
- Default Server: None is selected as the default. Click Select Server to select a PAC from the default PAC authority server or select a server from the Server group list. The EAP-FAST Default Server (PAC Authority) selection page opens.
NOTE: Server groups are only listed if you have installed an Administrator Package that contains EAP-FAST Authority ID (A-ID) Group settings.
PAC distribution can also be completed manually (out-of-band). Manual provisioning enables you to create a PAC for a user on an ACS server and then import it into a user's computer. A PAC file can be protected with a password, which the user needs to enter during a PAC import.
To import a PAC:
- Click Import to import a PAC from the PAC server.
- Click Open.
- Enter the PAC password. (Optional)
- Click OK closes this page. The selected PAC is used for this wireless profile.
EAP-FAST CCXv4 enables support for the provisioning of other credentials beyond the PAC currently provisioned for tunnel establishment. The credential types supported include trusted CA certificate, machine credentials for machine authentication, and temporary user credentials used to bypass user authentication.
Use a certificate (TLS Authentication)
- Click Use a certificate (TLS Authentication)
- Click Identity Protection when the tunnel is protected.
- Select one of the following:
- Use a user certificate on this computer. Click Select to choose the user certificate. Click OK. Proceed to Step 4.
- Use the certificate issued to this computer. Proceed to Step 5.
- Use my smart card. Select if the certificate resides on a smart card. Proceed to Step 5.
- User Name: Enter the user name assigned to the user certificate.
- Click Next.
Step 2 of 3: EAP-FAST Additional Information
If you selected Use a certificate (TLS Authentication) and Use a user certificate on this computer, click Next (no roaming identity is required) and proceed to Step 3 to configure EAP-FAST Server certificate settings. If you do not need to configure EAP-FAST server settings, click OK to save your settings and return to the Profiles page.
If you selected to use a smart card, add the roaming identity, if required. Click OK to save your settings and return to the Profiles page.
If you did not select Use a certificate (TLS Authentication), click Next to select an Authentication Protocol. CCXv4 permits additional credentials or TLS cipher suites to establish the tunnel.
Authentication Protocol: Select either GTC, or MS-CHAP-V2 (Default)
Generic Token Card (GTC)
GTC may be used with Server-Authenticated Mode . This enable peers using other user databases as Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) and one-time password (OTP) technology to be provisioned in-band. However, the replacement may only be achieved when used with the TLS cipher suites that ensure server authentication.
To configure a one-time password:
- Authentication Protocol: Select GTC (Generic Token Card).
- User Credentials: Select Prompt each time I connect
- On connection prompt for: Select one of the following:
- Static Password: On connection, enter the user credentials.
- One-time password (OTP): Obtain the password from a hardware token device.
- PIN (Soft Token): Obtain the password from a soft token program.
- Click OK.
- Select the profile on the Wireless Networks list.
- Click Connect. When prompted, enter the user name, domain and one-time password (OTP).
- Click OK.
MS-CHAP-V2. This parameter specifies the authentication protocol operating over the PEAP tunnel.
- User Credentials: Select one of the following options:
- Use Windows Logon: Allows the 802.1x credentials to match your Windows user name and password. Before connection, you are prompted for your Windows logon credentials.
NOTE: This option is unavailable if Pre-Logon Connect is not selected during installation of the Intel PROSet/Wireless software. Refer to Install or Uninstall the Single Sign On Feature.
- Prompt each time I connect: Prompts for user name and password every time you log onto the network.
- Use the following user name and password: The user name and password are securely (encrypted) saved in the profile.
- Roaming Identity: If the Roaming Identity is cleared, %domain%\%username% is the default.
When 802.1x MS RADIUS is used as an authentication server, the server authenticates the device that uses the Roaming Identity user name from Intel PROSet/Wireless software, and ignores the Authentication Protocol MS-CHAP-V2 user name. This feature is the 802.1x identity supplied to the authenticator. Microsoft IAS RADIUS accepts only a valid user name (dotNet user) for EAP clients. When 802.1x MS RADIUS is used, enter a valid user name. For all other servers, this is optional. Therefore, it is recommended to use the desired realm (for example, anonymous@myrealm) instead of a true identity.
Step 3 of 3: EAP-FAST Server
Authenticated-TLS-Server Provisioning Mode is supported using a trusted CA certificate, a self-signed server certificate, or server public keys and GTC as the inner EAP method.
Validate Server Certificate:
- Validate Server Certificate:
- Certificate Issuer: The server certificate received during TLS message exchange must be issued by this certificate authority (CA). Trusted intermediate certificate authorities and root authorities whose certificates exist in the system store are available for selection. If Any Trusted CA is selected, any CA in the list is acceptable.
- Allow intermediate certificates: The server certificate received during negotiation may have been issued directly by the CA or additionally by one of its intermediate certificate authorities. Select to allow a number of unspecified certificates to be in the server certificate chain between the server certificate and the specified CA. If cleared, then the specified CA must have been directly issued by the server certificate.
- Specify Server or Certificate Name: Select if you want to specify your server or certificate name.
The server name or a domain to which the server belongs, depends on which of the two options below has been selected.
- Server name must match exactly: When selected, the server name entered must match exactly the server name found on the certificate. The server name should include the fully qualified domain name (for example, Servername.Domain name).
- Domain name must end in specified name: When selected, the server name identifies a domain and the certificate must have a server name belonging to this domain or to one of its sub-domains (for example, zeelans.com, where the server is blueberry.zeelans.com).
NOTE: These parameters should be obtained from the administrator.
- Click OK to close the security settings.
EAP-FAST User Settings
NOTE: If an Administrator Package was installed on a user' computer that did not apply the Cisco Compatible Extensions, Version 4 Application Setting, only EAP-FAST User settings are available for configuration.
To set up a client with EAP-FAST authentication:
- Click Profiles on the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
- On the Profile page, click Add to open the Create Wireless Profile Wizard's General Settings.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the network identifier.
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive profile name.
- Operating Mode: Click Network (Infrastructure).
- Click Next to open the Security Settings.
- Click Enterprise Security.
- Network Authentication: Select WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise.
- Data Encryption: Select one of the following:
- TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message integrity check and a rekeying mechanism.
- AES-CCMP (Advanced Encryption Standard - Counter CBC-MAC Protocol) is used as the data encryption method whenever strong data protection is important. AES-CCMP is recommended.
- Enable 802.1x: Selected.
- Authentication Type: Select EAP-FAST to be used with this connection.
- Click Cisco Options to select Allow Fast Roaming (CCKM) which enables the client wireless adapter for fast secure roaming.
EAP-FAST User:
Select the credential retrieval method:
- Select the user credentials
- Use the Windows logon user name and password: The user credentials are retrieved from the Windows log on process.
NOTE: This option is unavailable if Pre-Logon Connect is not selected during installation of the Intel PROSet/Wireless software. Refer to Install or Uninstall the Single Sign On Feature.
- Prompt for the user name and password: Prompts for user name and password before you connect to the wireless network. The user name and password must first be set in the authentication server by the administrator.
- Use the following user name and password: The user name and password must be first set in the authentication server by the administrator.
- User Name: This user name must match the user name that is set in the authentication server.
- Domain: Name of the domain on the authentication server. The server name identifies a domain or one of its sub-domains (for example, zeelans.com, where the server is blueberry.zeelans.com).
NOTE: Contact your administrator to obtain the domain name.
- Password: This password must match the password that is set in the authentication server. The entered password characters display as asterisks.
- Confirm Password: Reenter the user password.
- Allow automatic provisioning of Protected Access Credentials (PAC):
EAP-FAST uses a PAC key to protect the user credentials that are exchanged. All EAP-FAST authenticators are identified by an authority identity (A-ID). The local authenticator sends its AID to an authenticating client, and the client checks its database for a matching AID. If the client does not recognize the AID, it requests a new PAC.
Click PACs to view any PACs that have already been provisioned and reside on this computer. A PAC must have already been obtained to clear Allow automatic provisioning on the Security Settings.
NOTE: If the provisioned Protected Access Credential (PAC) is valid, Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless does not prompt the user for acceptance of the PAC. If the PAC is invalid, Intel PROSet/Wireless fails the provisioning automatically. A status message is displayed in the Wireless Event Viewer that an administrator can review on the user's computer.
PAC distribution can also be completed manually (out-of-band). Manual provisioning enables you to create a PAC for a user on an ACS server and then import it into a user's computer. A PAC file can be protected with a password, which the user needs to enter during a PAC import.
To import a PAC:
- Click PACs to open the Protected Access Credentials (PAC) list.
- Click Import to import a PAC that resides on this computer or a server.
- Select the PAC and click Open.
- Enter the PAC password (optional).
- Click OK to close this page. The selected PAC is added to PAC list.
- Click OK to save the EAP-FAST settings and return to the Profiles list. The PAC is used for this wireless profile.
![]() ) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
![]() ) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
![]() ) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.
) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.

) in the Wireless Networks and Profiles list.









